Immune System Factors
There are 2 types of immunity: passive and active
Passive immunity occurs without the body’s immune response. They can be transferred between generations through DNA. Passive immunity also means that different species are often automatically immunized to pathogens that aren’t specialized to infect them.
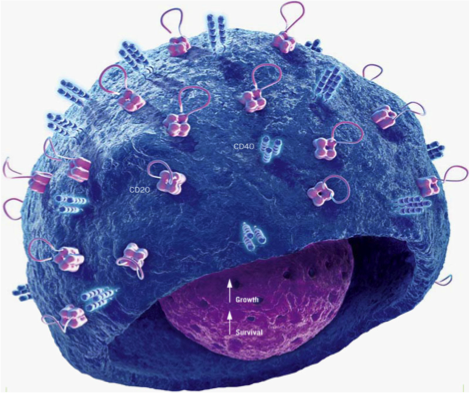
Active immunity occurs with body’s immune response. Acquired immunity is a type of active immunity. Humoral immunity is a type of immune response that depends on antibodies. It can cause the pathogens to burst, deactivate,or cause them to clump. First the pathogen binds to a B cell, then the antigen is put onto the B cell’s surface. A T cell then binds to the antigen part on a B cell, stimulating it to divide and differentiates into memory and activated B cells. Those activated B cells produce antibodies that cause the pathogens to clump, then phagocytes come and eat them, while memory B cells act as backup.
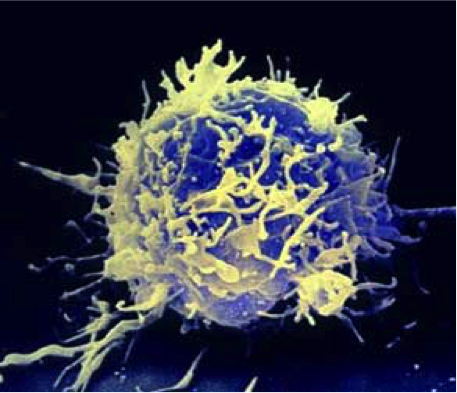
T-Cell
B-Cell