Anti-inflammatory Mediators
Both in-vitro and in-vivo studies suggest that this anti-inflammatory activity may be due to inhibition of several cytokines including tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα) and IL-1β, key mediators of the inflammatory response.
It has been reported that LF can destabilize the active form of tryptase in-vitro, a potential causative agent in inflammation.
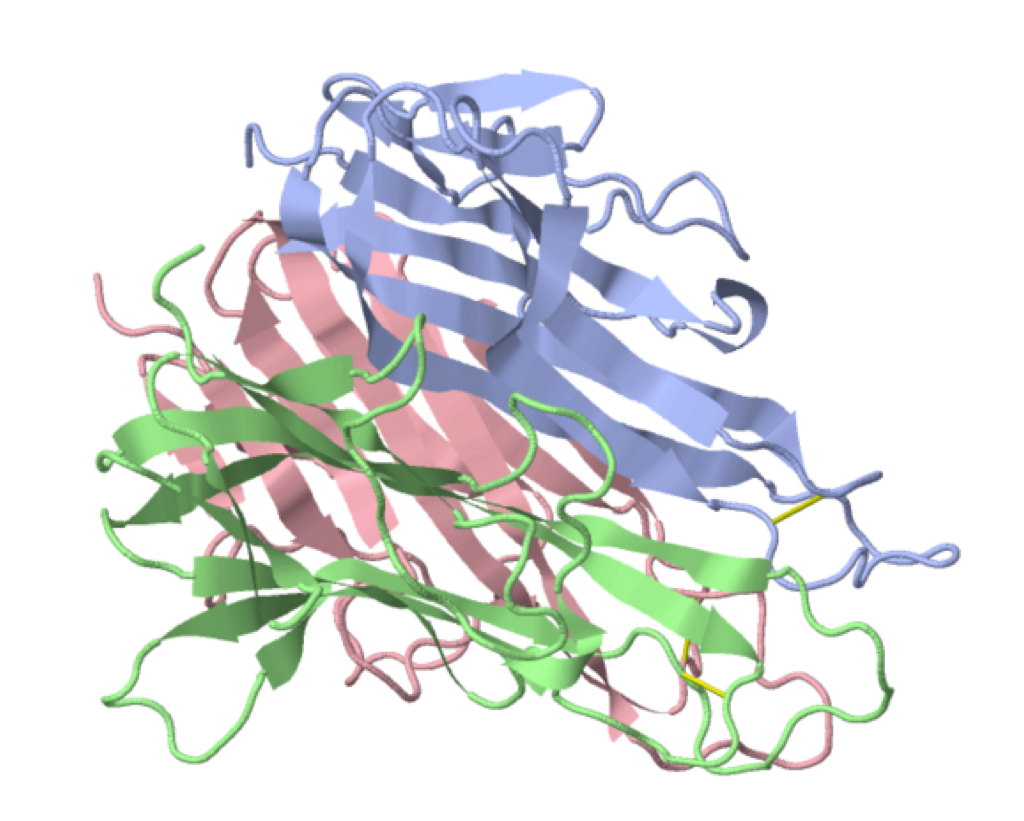
Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α)
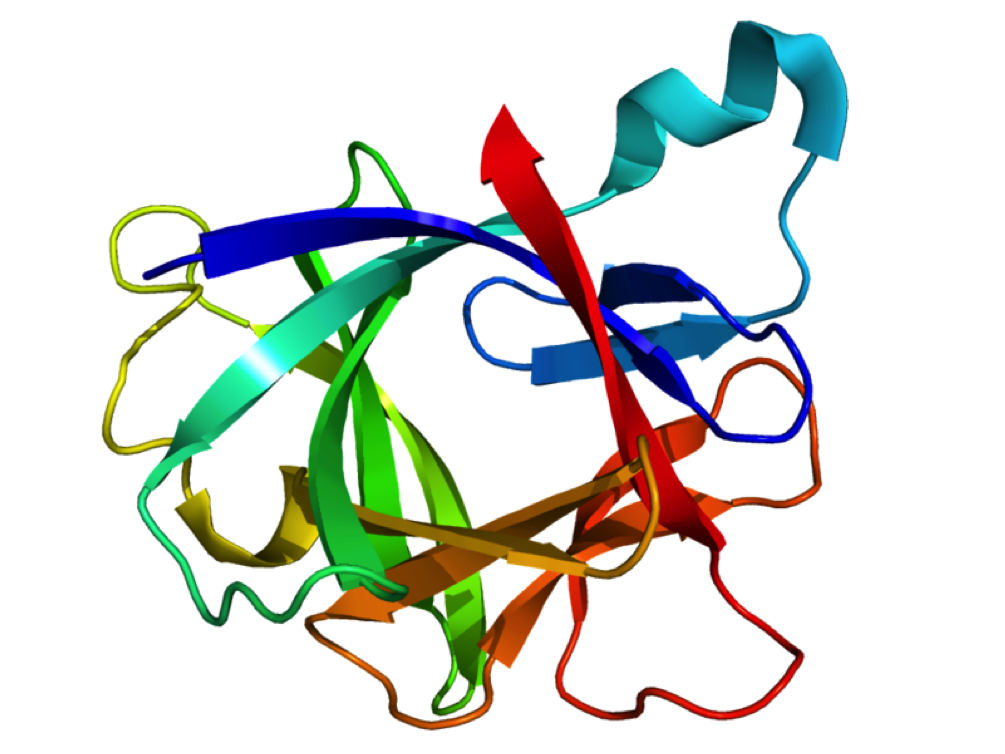
Interleukin 1 beta (IL1β)
References
1. Rhoades, C. J., Williams, M. A., Kelsey S. M. and A. C. Newland. (2000) Monocyte–macrophage system as targets for immunomodulation by intravenous immunoglobulin. Blood Reviews, 14:1, 14-30
2. Wong, K F., Middleton, N., Montgomery, M., Dey, M and Carr, R I. (1998), Immunostimulation of murine spleen cells by materials associated with bovine milk protein fractions. J-Dairy-Sci. 1825-32
