Epidermal growth factor for younger skin
Leading scientists have isolated an important polypeptide from colostrum known as Epidermal Growth Factor or EGF.
The word “epidermal” means skin. The EGF (Epidermal Growth Factor) in colostrum has the ability to stimulate the DNA and RNA to repair skin cells even when damaged by age, sun, chemicals or injury. There are very few sources for EGF and colostrum turns out to be one of the richest of them all.
Colostrum cream places these Epidermal Growth Factors on the surface of the skin cells, where they are rapidly absorbed through transdermal migration.
Once in the skin cells, EGF promotes rapid repair and regeneration, even in skin that has been badly damaged by age, sun, and chemicals.
Growth Factors in Colostrum
There is a range of various classes of growth factors including Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), Insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1), Insulin-like growth factor-2 (IGF-2), Epidermal growth factor (EGF) and Transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β).
Epidermal Growth Factor Functions
Helps to stimulate cell and tissue growth by stimulating DNA formation. Several studies show that these growth factors are capable of increasing T-cell production and accelerated healing.
Proliferation
Proliferation assay using different preparations of stabilized colostrum proteins and an immortalized epithelial cell line using the Alomar Blue Absorbance assay.
In Vilacto Bio™, a wide range of inflammatory abnormalities, inflammation related disorders (both acute and chronic) are in the capacity of our patented properties (Lactoactive®).
We have already overcome healing challenges for some concerns, like wounds, psoriasis, vitiligo, and other autoimmune related skin conditions and our products are currently available in markets as Vilact®. Our aim is to develop new drugs and treatments based on our strong resources to further skin healing for other conditions.
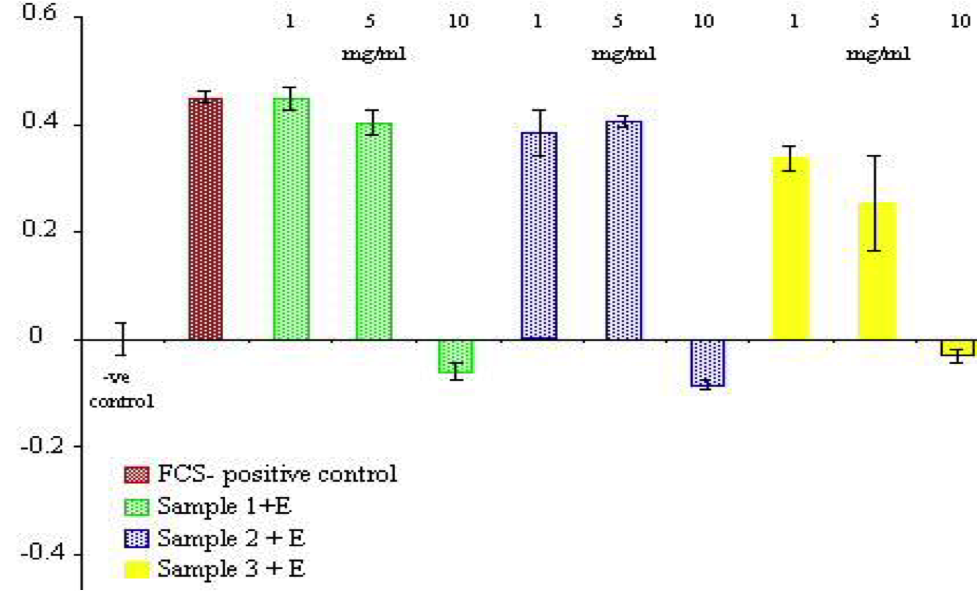
Epithelial proliferation cell assay with 3 preparations of stabilized colostrum (1+E, 2+E, and 3+ E).
References:
1. Elfstrand L.; Lindmark-Manson H.; Paulsson M.; Nyberg L.; Åkesson B. (2002)
2. Kelly, G.S.(2003)
3. Korhonen, H, Pihlanto, A. (2007)
4. Ballard, J.F., et al, (1982) Journal of Cellular Physiology, Vol.110, 249-254.
5. Robert Preston, N.D. The Complete Product Overview and Professionals Guide to Building Great Health.(2007)
